BACKGROUNDToxoplasmosis is one of the most typical meals borne zoonoses worldwide, and might be a severe life-threatening illness in the congenitally infected fetus and in immunosuppressed sufferers.
Among meals animals, sheep together with goats and pigs possess the best incidence of T. gondii cysts in meat, and play a main function as a supply of human an infection.
METHODSIn this examine, a new commercial ELISA kit (PrioCHECK Toxoplasma Ab SR, Prionics Schlieren-Zurich, Switzerland) for the detection of anti-T. gondii antibodies in serum, plasma and meat juice of sheep, was evaluated by evaluating it with the oblique fluorescent antibody check (IFAT), oblique haemagglutination check (IHA) and real-time PCR, on samples from experimentally inoculated and naturally uncovered sheep.
RESULTSThe commercial ELISA detected the an infection standing in 50% and 100% of sheep orally inoculated with 10,000 T. gondii oocysts (n = 6), from two or three weeks publish an infection (wpi), respectively, each on serum and plasma samples.
Meat juice from all experimentally inoculated sheep collected at slaughter (12 wpi) confirmed optimistic ELISA values. In naturally uncovered sheep (n = 396), the ELISA confirmed a superb settlement with IFAT (kappa = 0.91-1.0) and IHA (kappa = 0.96-1.0) carried out on serum; and a optimistic correlation was noticed between ELISA values and IFAT titers. By a Receiver Operating Characteristics (ROC) curve evaluation, the commercial ELISA had relative sensitivities between 93.33% and 100%, and relative specificities between 96.87% and 100% respect to IFAT and IHA, relying on the thought of cut-off worth and animal teams examined.
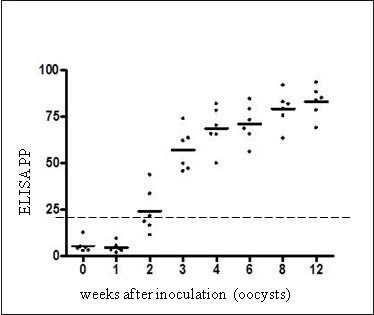
Furthermore, the ELISA appropriately acknowledged all animals reacting optimistic in real-time PCR.
The ELISA outcomes on meat juice agreed with these on serum samples in all experimentally inoculated animals, and in 94 out of 96 (97.9%) naturally uncovered sheep, when meat juice was examined at a 1:10 dilution.CONCLUSIONSThe commercial ELISA kit evaluated in this examine may symbolize a precious software to enhance the surveillance and reporting system for T. gondii in sheep populations on the farm degree or for analysis on the slaughterhouse, contributing to the management of this widespread zoonosis.
ELISA kits based mostly on monoclonal antibodies don’t measure whole IL-1 beta synthesis.
The paper by Herzyk et al. which seems in this situation of the Journal of Immunological Methods is a crucial and lengthy overdue contribution. The examine clearly and convincingly demonstrates that two broadly used commercial ELISA kits fail to detect over 90% of the 31 kDa human IL-1 beta precursor (pro-IL-1 beta) in varied cells.
This is because of the specificity of the monoclonal antibodies raised to the mature 17 kDa IL-1 beta and used in the commercial kits (or in ‘handmade’ ELISAs). The important quantity of pro-IL-1 beta which isn’t measured by the kits casts doubt on the accuracy of whole IL-1 beta synthesis reported in tons of of revealed research.
Investigators evaluating mobile synthesis of IL-1 in the event of new medication or IL-1 ranges in well being and illness more and more depend on commercial detection kits.
In this commentary, the significance and strategies for figuring out whole IL-1 beta synthesis are reviewed. In view of the preliminary optimistic outcomes reported on the success of the IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra) in scientific trials, consideration ought to be centered on the quantity of IL-1 produced in illness and on the stability of IL-1 versus IL-1ra synthesis. Thus, continued use of these ELISA kits which don’t detect pro-IL-1 beta will confound the interpretation of the IL-1 beta determinations.
